FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS ONLY.
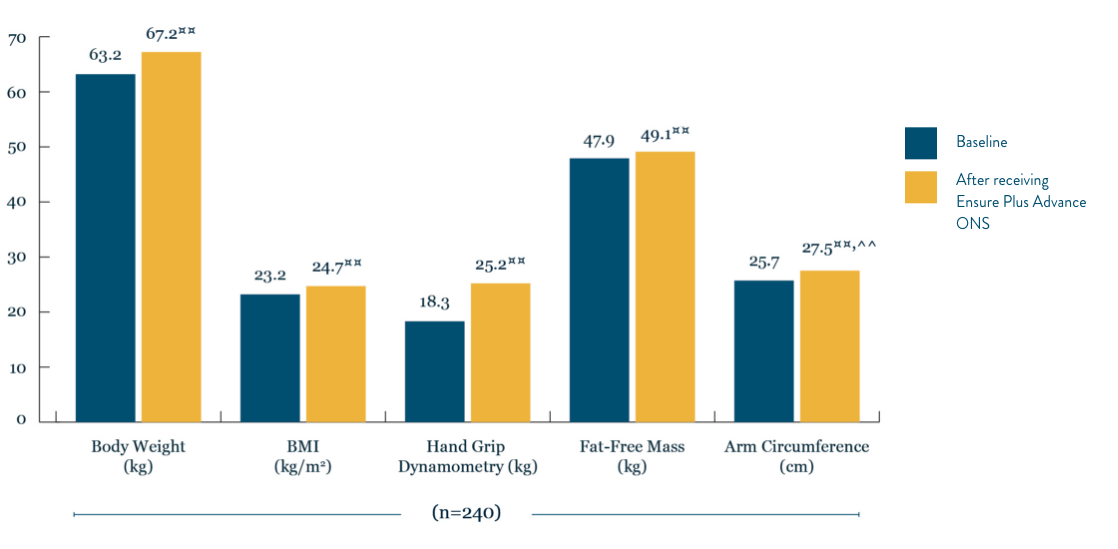
HMB, ß-hydroxy-ß-methylbutyrate. FOS, fructo-oligosaccharides. ONS, Oral nutritional supplement. IU, International Unit. MCT, medium-chain triglyceride. RTD, ready to drink. RTH, ready to hang. |Unique blend of highprotein, vitamin D and HMB. ◊Patients newly diagnosed with colorectal cancer. ◊◊Rounded up from 70.9%. ∂Rounded up from 44.9%. ∑Rounded up from 46.8%. **The ‘Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool’ (‘MUST’) isreproduced here with the kind permission of BAPEN (British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition). For further information on ‘MUST’ see https://www.bapen.org.uk/ Permission for the reproduction of ‘MUST’ is notan endorsement or recommendation for any commercially available manufactured products. LIC2104. †Research with 80 healthy women over 65 years of age supplemented with one serving of Ensure Plus Advance daily for 8weeks. ^In 92 patients aged 65 and over with hip fractures admitted to a rehabilitation facility, either receiving a standard diet plus 2 bottles of the study product or a standard diet only. Standard diet provided 1500 kcal, 87.4 gprotein a day. *In older community living adults (>60 years) receiving outpatient care with or at risk of, malnutrition. ‡In 62 community-dwelling pre-frail older people taking a specialised ONS vs nutritional counselling over 12weeks. §In 61 patients undergoing radical cystectomy receiving either a specialised ONS or vitamin/mineral supplement twice daily for 8 weeks. ¶An open-label study of elderly (n=35) patients with recent weight loss (>5% duringprevious 3 months) showed that 12 weeks supplementation of experimental product twice daily increased dietary intake, biochemical variables, and quality of life compared to baseline. ~As shown in a randomised controlled trial inwhich normally nourished patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchectasis received pulmonary rehabilitation plus a specialised ONS or pulmonary rehabilitation only for 12 weeks. In the intervention group, mean and maximumhandgrip dynamometry, physical functioning domain of QOL-B-V3.0 and other outcomes were significantly increased from baseline at 12 weeks and 24 weeks and fat free mass at 12 weeks. §§As shown in a randomised control trialto investigate the effects of a specialised ONS on older women (≥65 years) who underwent surgery for hip fracture vs. standard post-operative nutrition. Post-operative nutrition provided 1900 kcal and 76 g protein a day. Musclefunction was measured by handgrip strength. Mobilisation status was assessed on post-operative days 15 and 30. ***As shown in a randomised control trial to investigate the effects of the intervention ONS on malnourished,cardiopulmonary patients (≥65 years) vs placebo. The intervention ONS decreased mortality at 90 days post-discharge, however the study did not observe a significant effect for the primary composite endpoint of non-electivereadmission or death. This post-hoc, sub-group analysis from the NOURISH study cohort comprised 214 COPD patients. ††Strength was measured by handgrip strength in a post hoc analysis of over 600 malnourished people withheart or lung diseases, age 65 or older. Study product was consumed twice a day for 30 days, as compared to standard of care. ‡‡In 330 older adults with malnutrition and sarcopenia. Muscle quality was calculated as leg strengthexpressed relative to the muscle mass. #In a single arm open-label study of 148 patients aged 80±8.3 years with or at risk of malnutrition who consumed experimental product twice daily for 12 weeks as compared to baseline. ##Asshown in a randomised control trial to investigate the effects of the intervention ONS on malnourished, cardiopulmonary patients (≥65 years) vs placebo. The intervention ONS decreased mortality at 90 days post-discharge,however the study did not observe a significant effect for the primary composite endpoint of non-elective readmission or death. ∆Ensure Plus Advance is an oral nutritional supplement for frail elderly people (>65 years of age, witha BMI ≤ 23kg/m2), where clinical assessment and nutritional screening show the individual to be at risk of undernutrition. ΔΔResearch from 25 adults who were asked to drink 2 bottles of Ensure Compact a day for 7 days. Only 3out of 350 Ensure Compact bottles were not consumed. ¥A systematic review of 15 studies (n=943) published up to December 2021 including adult patients with various cancer types and treatments consuming HMB-ONS (EnsurePlus Advance or Juven/Abound) for 10 days-6 months. ¤¤p< 0.05 vs Base. ^^p < 0.05 vs ONS obtained from the adjusted model. ¤¤¤Improvements in handgrip strength were higher in patients receiving Ensure Plus Advance vsstandard oral nutritional supplements. Retrospective database review of 283 patients (63% with cancer) with or at risk of malnutrition who received 2 daily servings of Ensure Plus Advance or standard oral nutritional supplementsin combination with dietary counselling and exercise for 3-6 months. Handgrip strength: 6.2 vs. 4.7 kg; p>0.05. ◊◊1/2 higher quality studies showed benefit on cancer therapy-related toxicity. ∆2/5 higher quality studies showedbenefit on body weight with a dose of 3 g/ day of Ca-HMB over 4–24 weeks in patients with cancer.
References: 1. Wolfe RR Am J Clin Nutr 2006;84:475-482. 2. Caillet P et al. Clin Nutr 2017;36:1473-1482. 3. Hebuterne X et al. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2014;38(2):196-204. 4. Ryan AM et al. Proc Nutr Soc 2016;75(2):199-211.5. Cancer Research UK, 2020. www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/coping/physically/diet-problems/types/cachexia Cachexia (wasting syndrome) | Coping with cancer | Cancer Research UK). Last accessed February 2023. 6.Christensen JF et al. Annals of Oncology 2014;25:947–958. 7. Barret M et al. Eur J Surg Oncol 2014;66:583–589. 8. Findlay M et al. J Acad Nutr Diet 2020;120(8):1330-1347. 9. Baracos VE et al. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;91(suppl)1133S-1137S. 10. Tan BH et al. Eur J Surg Oncol 2015;41:333–338. 11. Trejo-Avila M et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021;36(6):1077-1096. 12. Lieffers JR et al. Br J Cancer 2012;107(6):931-936. 13. Real GG et al. JPEN 2018;42(8):1272-1279. 14. Krznaric Z et al. Clin Nutr 2020;39:1983-1987. 15. Ritch CR et al. J Urol 2019;201(3):470–477. 16. Cornejo-Pareja I et al. Nutrients 2021;13(12):4355. 17. Deutz NE et al. Clin Nutr 2014;33(6):929-936. 18. European Food Safety Authority. EFSA J 2011;9(9):2382. 19. Berton et al. PloS one 2015;10(11):e0141757. 20. Chavarro-Carvajal DA et al. Clin Nutr ESPEN 2022;48:291-297. 21. Peng LN et al. J NutrHealth Aging 2021;25(6):767-773. 22. Malafarina V et al. Maturitas 2017;101:42-50. 23. De Luis DA et al. Nutr Hosp 2015;32(1):202-207. 24. Olveira G et al. Clin Nutr 2016;35(5):1015-1022. 25. Deutz NE et al. Clin Nutr 2021;40(3):1388-1395. 26. Matheson EM et al. Clin Nutr 2021;40(3):844-849. 27. Cramer JT et al. JAMDA 2016;17(11):1044-1055. 28. Ekinci O et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2016;31(6):829-835. 29. De Luis DA et al. Eur Geriatr Med 2018;9(6):809-817. 30. Deutz NE et al. Clin Nutr 2016;35(1):18–26. 31. Prado CM et al. J Cachexia, Sarcopenia Muscle 2022;13:1623–1641. 32. Data on file. Abbott Laboratories Ltd, 2013 (Ensure Compact Compliance Research). 33. Nelson JL Clin Nutr Exp 2019;28:123-130.






.png)







.png)